Fri, Mar 3, 2023 12:00 AM
Polyester fabric vs. Natural fabric resources consumption
The textile industry plays an essential role in our daily lives and the global economy, producing a variety of fabrics for clothing, home goods, and industrial applications. However, the production of textiles is a resource-intensive process that consumes significant amounts of water, land, energy, chemicals, and raw materials.
The textile industry plays an essential role in our daily lives and the global economy, producing a variety of fabrics for clothing, home goods, and industrial applications. However, the production of textiles is a resource-intensive process that consumes significant amounts of water, land, energy, chemicals, and raw materials. This can have substantial environmental impacts, including water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and the degradation of land and other natural resources.
As the demand for textiles continues to grow, it's important to understand the resources used in the industry and their impact on the environment. In this article, we'll explore the various resources consumed by the production of polyester compared to natural fabrics such as cotton, wool, and silk, including demonstrating the environmental impacts that may result from the production processes in the textile industry.
Resources consumption
1. Polyester
Polyester is a synthetic fabric made from a polymer called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It's a popular material in the textile industry due to its low cost, durability, stretchability, and resistance to shrinking and wrinkling. Polyester is widely used in clothing, bedding, towel, stuffed toy, upholstery, and outdoor gear due to its ability to retain its shape and color.
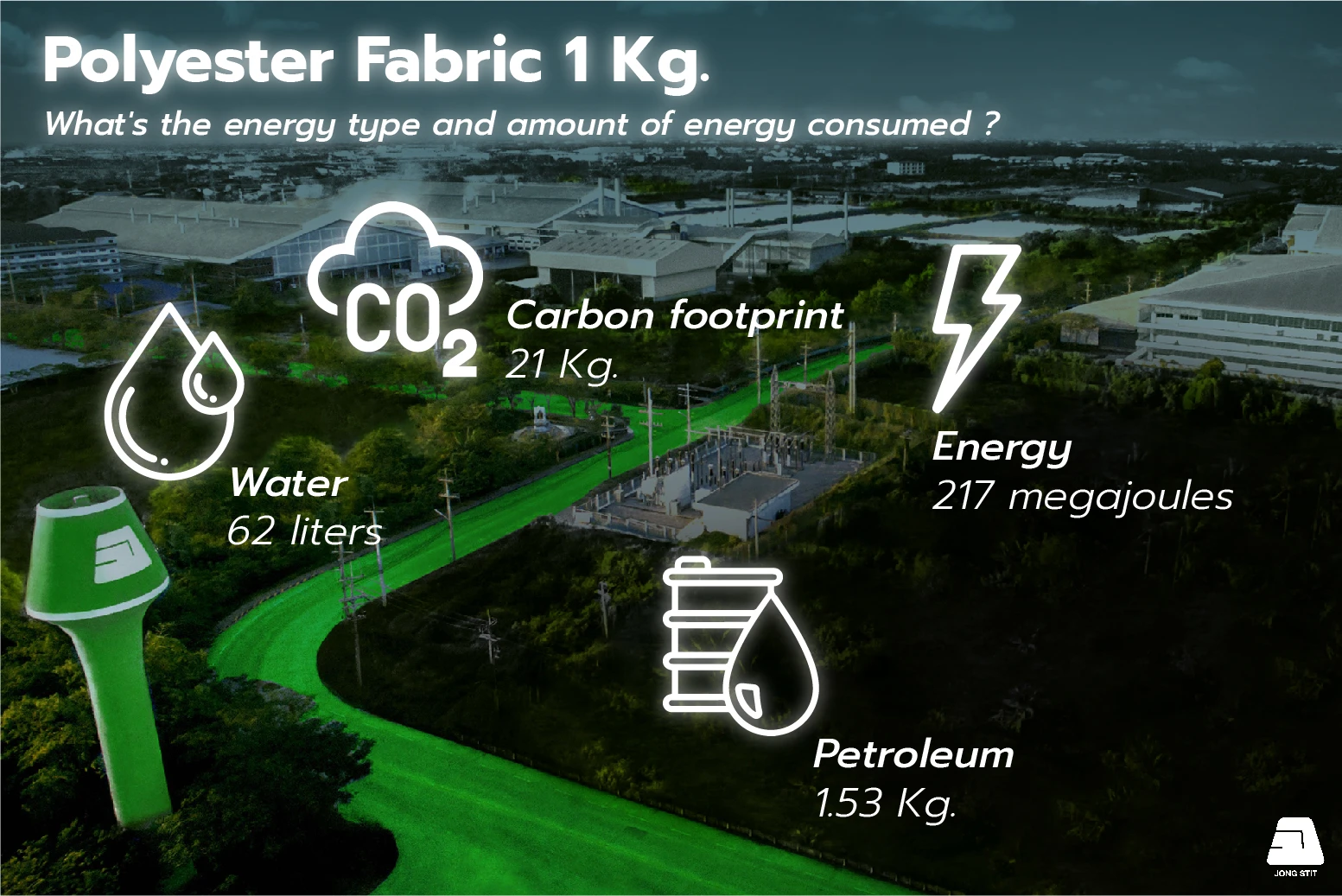
Kilogram of Polyester resources consumption
1.1 Energy : The energy used to produce polyester is estimated at around 217 megajoules. This figure includes the energy used for producing polyester fiber and the fabric.
1.2 Petroleum : Polyester fabric is typically made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) derived from petroleum. Polyester used 1.53 kilograms of petroleum as raw material. These materials are processed and converted into the polymer that makes up polyester fibers and then processed into the fabric.
1.3 Water : Polyester fabric production consumes 62 liters of water for various purposes, such as washing or processing the raw materials, dyeing, and finishing the fabric.
1.4 Carbon footprint : Polyester fabric manufacturing process emits 21 kilograms of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
2. Cotton
Cotton is a natural fabric derived from cotton seeds. The fiber is used to make various products, including clothing, bed sheets, towels, and more. Cotton is well-known for its softness, breathability, and absorbency. It's also relatively easy to dye and can be blended with other fibers creating textiles in different textures and weights.
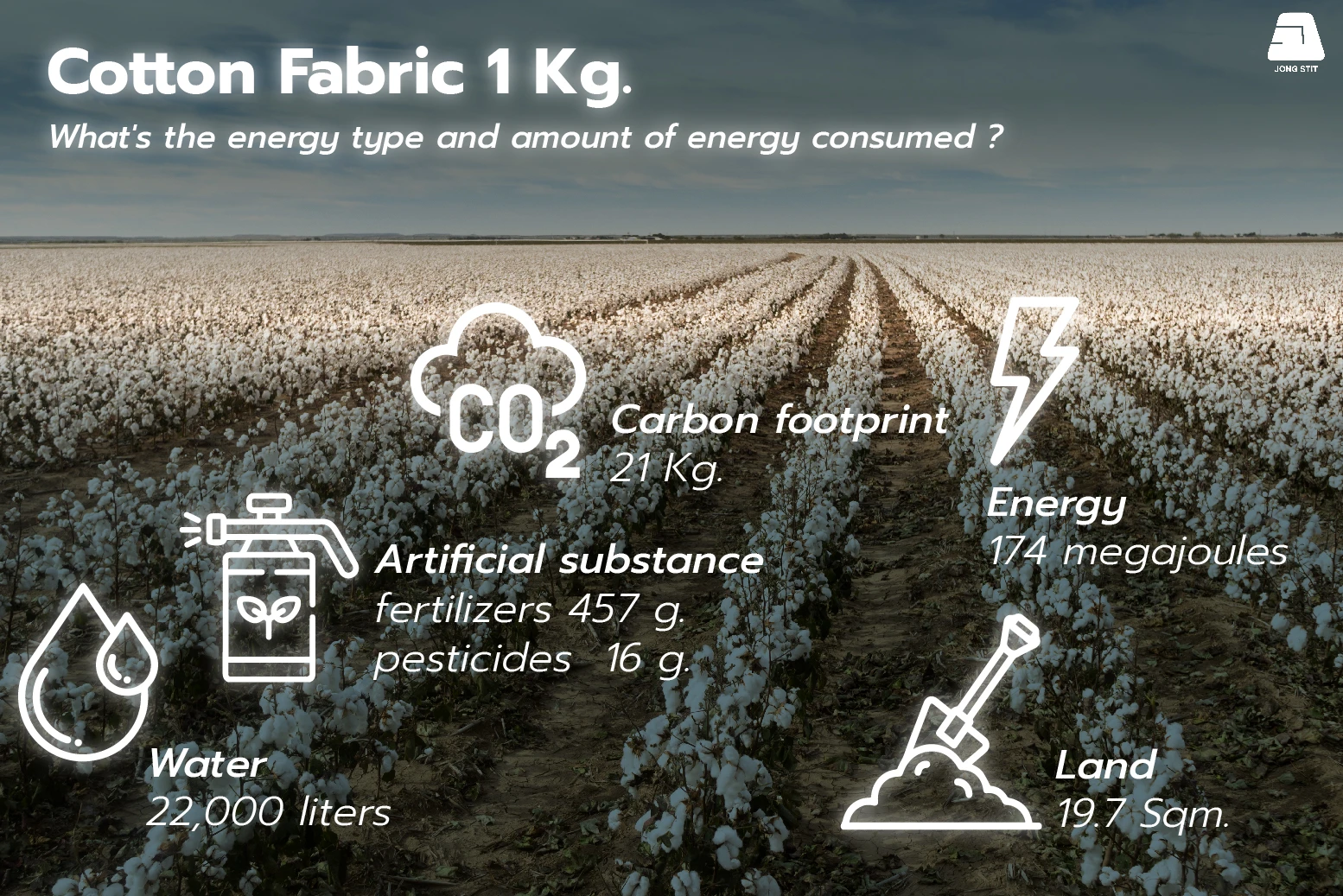
Kilogram of Cotton resources consumption
2.1 Energy : The energy used in producing cotton fabric is around 147 megajoules. These energies used since the beginning from growing cotton trees, processing the fiber and manufacturing the fabric.
2.2 Land : Cotton requires an average of 19.7 square meters for growing and cultivating.
2.3 Water : It takes more than 22,000 liters to manufacture 1
kilogram of cotton, equivalent to just 1 T-shirt.
2.4 Fertilizers and Pesticides : The production of cotton demands artificial fertilizers at around 457 grams and 16 grams of pesticides. These chemicals can contribute to soil degradation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss and pose risks to the health of farmers and other workers who handle these chemicals.
2.5 Carbon footprint : Producing cotton fabric emits 27 kilograms of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
3. Silk
Silk is a natural fabric produced by certain insects, most notably silkworms which then transform into cocoons. The fiber is obtained from the cocoons and processed into thread for textiles. Silk is prized for its softness, luster, rich feel, lightweight, strong, and hypoallergenic. These make it a popular material for high-end clothing, bedding, and accessories.

Kilogram of Silk resources consumption
3.1 Energy : The energy usage producing raw silk is around 1,843 megajoules. It requires a significant amount of energy, mainly in heat, to carry out the various stages of the silk production process, such as reeling, degumming, and twisting.
3.2 Water : From the first phase, silk needs about 1,000 liters, consisting of mulberry cultivation, silkworm rearing, cocoon processing, and dyeing and finishing.
3.3 Land : An estimated 200 kilograms of mulberry leaves are needed to feed silkworms, which can be planted on about 80 square meters of land.
3.4 Fertilizers and Pesticides : Around 0.04 kilograms of pesticide and 3,000 kilograms of fertilizer are used to prevent pests and grow mulberry trees.
3.5 Carbon footprint : Silk production process emits 25 kilograms of carbon dioxide into the air.
4. Wool
Wool is a natural fabric made from sheep fleece. It's one of the oldest, long histories, and most used materials in clothing and home textiles. This fiber is prized for its softness, warmth, and durability. Wool fabric is commonly used for many ideals, including suits, jackets, coats, blankets, and rugs.

Kilogram of Wool resources consumption
4.1 Energy : Wool fabric used the energy of around 155 megajoules. Started with raising, shearing sheep, and processing the wool fibers into the fabric.
4.2 Water : The typical water used worldwide to produce wool is around 170,000 liters. It takes a high amount of water not only for raising the sheep but also for processing the raw wool into clean wool suitable for textile production.
4.3 Land : The average weight of wool taken off a sheep is measured at around 3 kilograms annually. Hence, you need at least 4,000 square meters of grazing land to raise a sheep to produce wool. Land clearing for sheep farming is a complex issue with environmental impacts. In some regions, such as Australia, land clearing for sheep farming has been a major contributor to deforestation and habitat loss, leading to declines in native wildlife populations and increased soil degradation.
4.4 Carbon footprint : Wool fabric discharges 46 kilograms of carbon dioxide into the air from the beginning process.
Conclusion
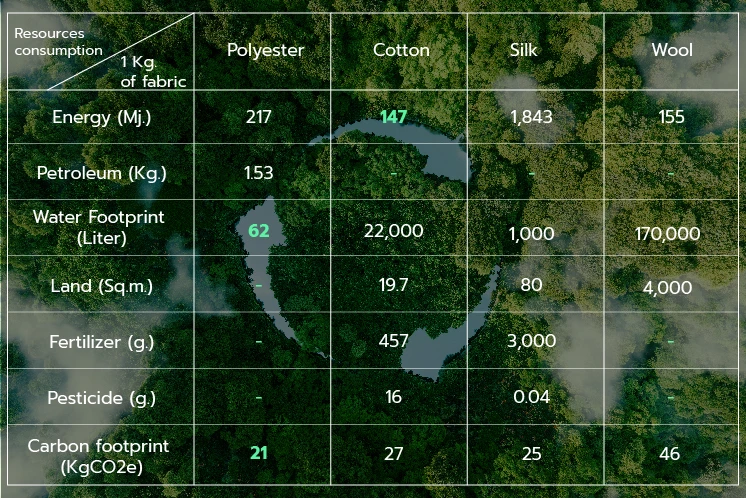
The table shows each fabric production with different resource consumption and environmental impact. Even though polyester fabric uses petroleum as a raw material, it requires other resources less than natural fabrics. Besides, when considering the resources consumed by natural fabrics, it can be found that they need a large number of natural resources.
For example, 1 kilogram of silk fabric production requires energy up to 1,843 megajoules. Cotton fabric uses up to 22,000 liters of water. And wool fabric uses up to 170,000 liters of water.
As well as, land usage for cultivation or animal rearing can lead to soil degradation, chemical water contaminants, deforestation, habitat loss for endemic species, and more.
Consequently, to reduce the environmental problems that our world is facing, it's our responsibility to choose fabric or textile with the least possible environmental impact to save resources and minimize waste released into the atmosphere.
Ref.
https://oecotextiles.blog/2009/06/16/what-is-the-energy-profile-of-the-textile-industry/
https://blogs.nicholas.duke.edu/citizenscientist/the-fabric-for-our-lives/
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Performance-of-1-kg-of-cotton-and-polyester-fabrics-over-a-period-of-two-years-59_tbl3_262946333
https://www.puresilkduvet.com/Help/Info/Silk-Production#:~:text=Around%20500%20silkworms%20or%2080,1%20kg%20of%20raw%20silk.
https://www.woolfacts.com/is-wool-sustainable/water-use/#:~:text=It%20takes%20a%20whopping%20170%2C000,litres%20of%20water%20per%20kilogram.
https://blog.aghires.com/sheep-facts/
https://www.hobbyfarms.com/5-questions-to-ask-before-keeping-sheep-3/#:~:text=A%20general%20rule%20of%20thumb,may%20not%20support%20even%20one.
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Mass-and-energy-flow-in-silk-production-Mass-values-and-contribution-to-energy-demand_fig2_263238924
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/254/19/192008/pdf








